Introduction
An intermodal container is a large standardized shipping container, designed to travel long distances for long periods of time. It can be used with different types of transportation from freight transport to railways and trucks. These containers have to be extremely durable, to protect the cargo contained inside and not to get worn out during its long years of operation. It is not rare for these containers to get dropped on occasion, during the handling. In this case study, we would like to look into the behavior of the container during the drop from 5m.
Geometry and mesh
Ninety percent of the global container fleet are so-called "dry freight" or "general purpose" containers. These are durable closed steel boxes, mostly 12m in length and 2.6m in height. Since the majority of the parts of the container are made from sheet metal, shell elements were used for the finite element model. Shell elements dramatically decrease the number of degrees of freedom in the model, which was very welcoming, since we used an explicit scheme for the analysis.

During the meshing, we always have to consider some kind of compromise when using explicit analysis. The time step of the analysis depends on the smallest element in the whole model. This encourages us to have a mesh cell size as even as possible.

Loads and Boundary conditions
Loads and boundary conditions are quite straight forward when it comes to drop test simulation. We only have to assign the initial velocity and prescribe the rigid ground. When using explicit scheeme, the contacts are automatically generated.
Results
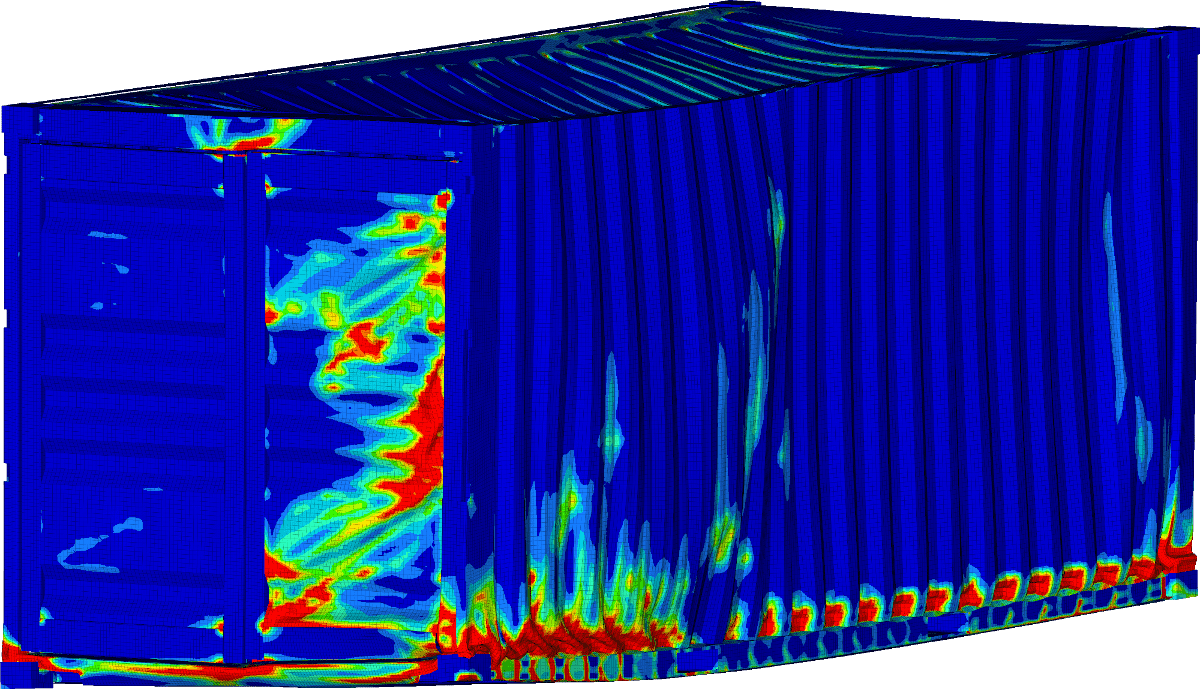
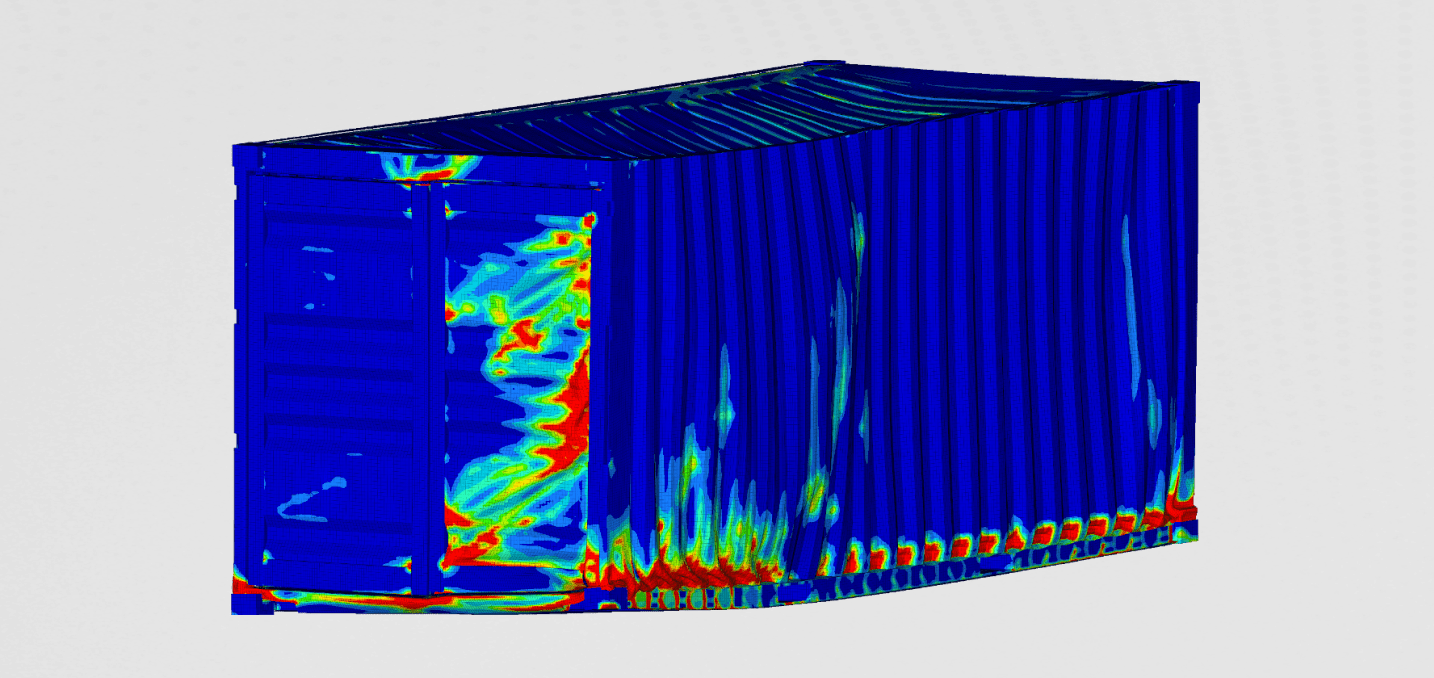
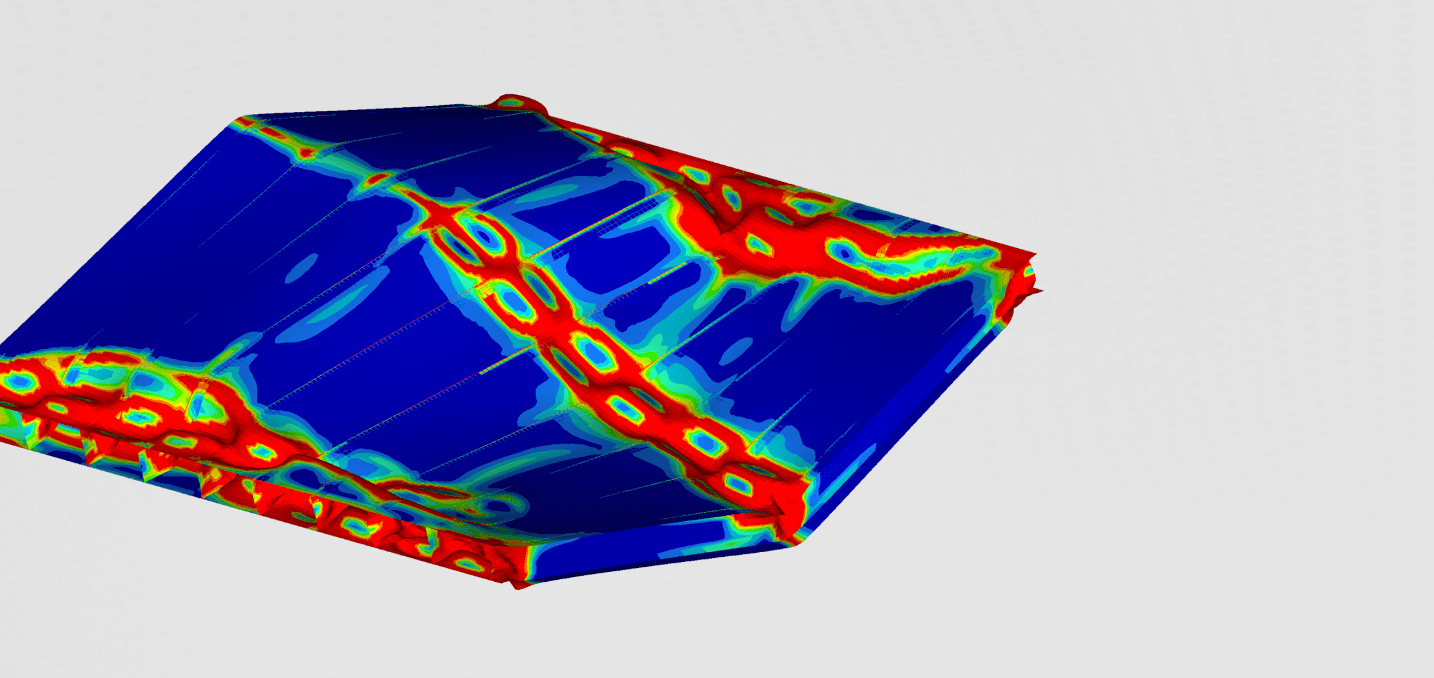
We were mostly interested in the structural integrity of the container during the drop. Stresses, strains, and plastic deformation were some of the results we were interested in. Besides that, we were also monitoring the acceleration inside the container. This data would be useful for the cargo that is transported inside such a container.




In Figure 4 the graph od the vertical acceleration in the center of the container is plotted. The reader can also observe the peak acceleration inside the container.

We also observed the plastic deformation after the drop. This gives us information about the overall damage of the container after the drop.